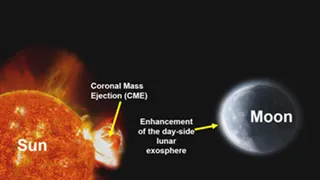
Updated: Sun, 19 Oct 2025 03:10 (IST) India’s Chandrayaan-2 mission used its scientific instruments to observe the effects of the Sun’s coronal mass ejection (CME) on the Moon for the first time. Chandrayaan-2 mission was launched in 2019. Will help understand the effect of space weather on the Moon (Photo- X ISRO) PTI, Chennai. India’s Chandrayaan-2 mission used its scientific instruments to observe the effects of the Sun’s coronal mass ejection (CME) on the Moon for the first time. Chandrayaan-2 mission was launched in 2019. Chandrayaan-2 carried eight payloads ISRO said on Saturday that this observation will help understand the moon’s exosphere, the moon’s extremely thin atmosphere and the effect of space weather on its surface. Chandrayaan-2, which was launched from Sriharikota on July 22, 2019, was carrying eight payloads. Remove Advertisement Only Read News On 2019, Chandrayaan-2 was placed in the Moon’s orbit. On August 20, 2019, Chandrayaan-2 was placed into the Moon’s orbit. Although communication with the Vikram lander was lost during the landing attempt, the orbiter is still fully functional. According to ISRO, Chandra Atmospheric Compositional Explorer 2, one of the payloads on board Chandrayaan-2, recorded the effects of coronal mass ejection from the Sun on the lunar exosphere. Coronal mass ejections are the most powerful explosions in the Solar System. The Sun emits helium and hydrogen ions during coronal mass ejections. Coronal mass injection has a major impact on the Moon. This is because the Moon has no air and no large magnetic field, which can protect its surface to some extent from the Sun’s influence. Observations by Chandra Atmospheric Compositional Explorer 2 revealed that the effects of the Sun’s coronal mass ejection increased the total pressure of the Moon’s exosphere (extremely thin atmosphere) during the day. This increase is consistent with earlier theoretical models that predicted such an effect, but this is the first time a payload on Chandrayaan-2 has observed such an effect. A rare opportunity to directly observe the impact of a coronal mass ejection (CME) on the Moon arrived on May 10, 2024.
Chandrayaan-2 achieved a major feat, seeing the effect of Sun on the Moon for the first time; ISRO Showed Live – Chandrayaan 2 observed the solar effect on the moon for the first time