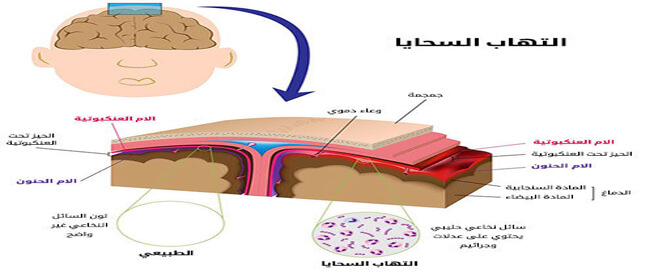
Meningitis, sponsored by meningitis, is an inflammatory disease that affects the mucous membranes that surround the brain, and spilled cord due to bacterial or viral infection. Types of meningitis The functioning and symptoms of the disease vary depending on the type, and meningitis contains the following types: 1. Bacterial meningitis There are good possibilities for recovery without any side effects, and the possibilities of complete recovery are estimated at 90%, provided the treatment is done at an early stage. The factors that can affect the possibilities of healing are mainly the health of the patient, or a delay in treating treatment, or a germ of a fierce tension more than usual. 2. Aseeptic Mongitis has not yet succeeded in determining the cause of this type of inflammation, in their efforts to cultivate it in a cultivation after a sample of body fluids was taken by the name. The cause is usually a viral, but in a small part of cases, another cause of pollution such as parasites speaks. 3. Viral meningitis is the most common viruses as meningitis is enterrovirus. There are other common viral causes, which are arbovirus viruses, the second -style oral herpes virus (herpes simplex type 2), and human immunological virus (HIV). Infection arising from the intero virus, and viruses transmitted with arthropods are of a seasonal nature, and its spread is significantly in the summer. The nature of the course of the disease is benign, fever and head pain fades within about a week, and with the exception of a few rare cases, healing has been completed in most of the cases. Symptoms of meningitis in the following are the most important symptoms of meningitis: 1. Symptoms of general meningitis are one of the most famous symptoms that a meningalist patient suffers from the following: light phobia (photophobia). The fever. Tip as you move the neck. Change to the degree of awareness of nausea and vomiting. Seizure. Skull neuropathy. Hyper irritation in children. Eating habits in children. 2. Symptoms of sterile meningitis are common symptoms of sterile meningitis: headaches. nausea. General weakness. Struggling to move the nickname. Causes and factors of the risk of meningitis There are many causes, and factors that increase the risk of illness. 1.. The causes of meningitis There are many germs that cause meningitis, which are as follows: Ordinary germs include causes of meningitis: pneumococci: one of the most common inflammatory generators responsible for almost half of cases. Meningococci: Sometimes a widespread result of purple -colored prominent points is made. Haemophilus: The appearance of this bacterium is in a continuous response, as the vaccination has become acceptable and even recommended for children. Injuries with these three germs form 80% of all cases of bacterial infection. Unlimited bacteria are the least common bacteria that cause disease: Streptococcus B: Most of the patients are children under the age of one month. Listeria: Is the cause of the disease in the middle of the new and the elderly. Staphylococcus: inflammation if exposed to stoning injuries in the head, or undergo a phase of the head. 2. The risk factors that have the most of the disease develop the disease are the group of people with the following diseases: internal otitis. Sinusitis. The inflammation of the lungs. Endocarditis. Cirrhosis. alcoholism. Mile in the blood cells. The work of the work of the immune system. Cerebrospinal fluid caused leakage near the infection. Complications of meningitis are complications of meningitis: hearing loss. Epilepsy. Memory problems. Brain damage. Migraine. Diagnosis of meningitis, since the disease is a threat to the life of the injured, the rapid diagnosis and immediate treatment are subsequently mandatory. 1. Diagnosis of meningitis in general. The patient’s narrative of the symptoms and signs of inflammation that occur when examined are likely to cause suspicion about the presence of the disease at an early stage. If you take a sample of the cerebrospinal fluid that examines the chosen to confirm the suspicion is to take a sample of the cerebral cerebral fluid through the waist, the presence or absence of the disease is determined, depending on the fluid analysis in the laboratory. The following results support the presence of the disease, such as: The large number of white cells, especially neutrophils, that is, a number of hundreds of hundreds and even 10,000 cells per cubic millimeter. Glucose level without the natural relationship. Protein ratio is higher than normal. Determine the cause of the disease. The causes of the disease can be identified in different ways, including: Direct viewing under a microscope. Distinctive color when using special dye products. Agriculture in the developer. The genetic fingerprint of each enemy is followed. 2. Diagnosis of sterile brain membranes. Lumbar puncture is to take a sample of the cerebrospinal fluid is the general and general method of confirming the diagnosis. Screened signs of cerebral cerebral fluid in viral inflammation: a large large number of white blood cells, with a number of 10-1000 per millimeter cubic, mostly of the type of lymphocytes. Proper values for glucose and protein ratio and protein can sometimes be slightly high. This is followed by trying to take a sample of the virus from different body fluids, such as: cerebrospinal fluid, blood, urine, stools and mucous membranes in the pharynx. The cultivated is often sterile, so that the identity of the inflammation generation cannot be conceived. The polyrase chain reaction – PCR enables the exact identification of the inflammatory generator and can be used if necessary. The treatment of meningitis of the immediate follower of the treatment of early meningitis as possible with antibiotics immediately after the concession and before determining the identity of the disease generator. The treatment of meningitis in general 1. Antibiotics, and antibiotics used for treatment are: ceftriaxone: which is given intravenously in a dose of 4 grams per day. Cefotaxime: It is given intravenously in a dose of 12 grams per day. Penicillin: Add the pennyline intravenous for children and the elderly in a dose of 12 grams per day. Vancouveromycin: It is added in a dose of 2 grams per day, in cases of inflammation after head injury or after medical procedures. 2. Corticosteroid was recently discovered that the percentage of deaths drops, and the risk of permanent disability among adults with the brain tissue with high pressure within the cranial, by adding a Dexamethason type. Determining the infection generator and its sensitivity to estimate the different medicines that enable the continuity of treatment with the optimal agent. Treatment of sterile meningitis The treatment is often supportive, such as treatment with pain, intravenous and easy symptoms that the patient suffers from. Prevention of meningitis The meningitis can occur in the following methods meningitis: 1 Vaccination has contributed routine vaccination against the honorable sustainable used in the middle of children by reducing the incidence of significantly generated meningitis. People who were close to a patient diagnosed as a meningitis should be vaccinated as a result of meningitis, with the aim of reducing the risk of spreading the disease. 2. Antibiotics of the follower of oral antibiotic therapy of the following types: rifampine in a dose of 600 milligrams twice a day for two days. Ciprofloxacin in a dose of 500 milligrams once a day for one day. The antibiotic for infection prevention is used for people who were close to patients with the disease, whose causes were determined, such as meningor or sustainable grief.
Menantitis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment