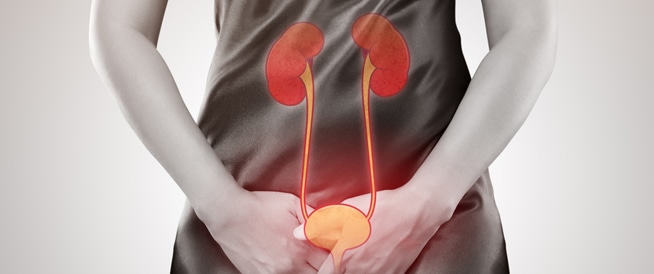
Returning urinary tract infection – UTI sponsored by regular inflammation of the urinary tract, a widespread pathological condition, especially in women, where about 30% of all women are exposed to at least one case of urinary tract infection during their lives, and 20% of them are the condition that occurs again, and 20% of women suffering to urinary bleaching. The difference between acute inflammation and regular inflammation includes the difference as follows: 1. Acute inflammation is defined as a new infection in the urethra, the bladder or kidneys, and this inflammation disappears within a short period of treatment. 2. Repeated inflammation in the urinary tract is the infection that occurs after a state of acute inflammation due to the same type of bacteria that caused the first inflammation, or even because of another type of germs, in this group 80% of those suffering from urinary tract infection in the next year and a half. Symptoms of regular urinary tract infection include symptoms of regular urinary tract infection: pain in the lower area of the abdomen that occurs during urination or without urination. Pain and heartburn during urination. Urinary urgency. Repeated urination and pain in the loins. High temperature. It is important to note that during pregnancy there is a greater possibility of urinary tract infection and that this inflammation is also more dangerous. Kidney inflammation occurs at a higher rate, thus the presence of germs and viruses in the urine during pregnancy, even if it is very low that requires immediate treatment. Causes and factors of the risk of regular urinary tract infection in the following are an exposition of the most prominent causes and risk factors: 1. The causes of regular urinary tract infection in women who are repeatedly infected and urinary tract infection is the process of bacterial correlation with the mucous membrane in the vagina, as one of the lasting theory is regained. of the tendency to repeat infection is a genetic cause. In most cases, the gut bacteria that multiply near the urethra and cause infection, while these bacteria of the urethra come to the bladder and even the kidneys, are the reason behind the presence of urinary tract inflammation and infection. The main features of these germs that cause urinary inflammation are their ability to stick to the mucosa in the urinary tract, as this feature is the most infection that causes infection in the urinary tract, which is Escherichia coli, which is involved in 85% of urinary tract infections. 2.. Urinary tract infection factors include risk factors that can result in regular urinary tract infection. The following: Reduced hormonal activity in menopause. Diabetes. Immune system defect. Urine flow disorders, where regular urine flow disorder gets the kidneys to the bladder and from there. Sex. Previous history of urinary tract infection. The use of female isolation during sex. Use oral contraceptives. Use of spermicides. Hormonal changes during menopause. The complications of regular urinary tract infection if the infection remains without treatment. The infection can spread to the kidneys and lead to permanent kidney damage, which is more dangerous, as if a person has a kidney infection, he may need treatment in hospital. Chronic urinary tract infection rarely causes blood rot if left without treatment, which can threaten life. Diagnosis of repeated urinary tract infection The urinary tract infection is diagnosed depending on the characteristic complaints associated with it, depending on the physical examination and examination of urine samples. The most prominent diagnostic methods include the following: urine transplant test: It is achieved from the presence of bacteria in the urine. Computerized tomography of the urinary tract: It allows the doctor to see the urinary tract with more details. Treatment of regular urinary tract inflammation The treatment of regular urinary tract infection depends on antibiotics (antibiotic) antibacterial agents that cause inflammation, where the type of treatment is chosen, including: the age of the injured. Other diseases he suffered. Disadvantages in urinary tract. Kidney performance. Pregnancy. Allergy to antibiotics. Inflammation. The type of germs and its sensitivity to the medicine. The type of antibiotic is selected depending on everything mentioned above, and the duration of the treatment is short and the treatment is done by mouth or venous injection. Regular urinary tract infection prevention has discovered that cranberry juice or the concentrated juice affects a positive effect and contributes to the prevention of regular infection with urinary tract infection, as other prevention methods include: urination before and after gender. Clean the gender and genital areas before and after sex. Drink plenty of water to expel bacteria from the bladder. Look for alternatives to membranes or sperm for birth control. Wear cotton underwear and loose clothing. Wipe from front to back to the toilet. Avoid perfumed body wash or vaginal shower.
Repeated inflammation of the urinary tract: symptoms, causes and treatment