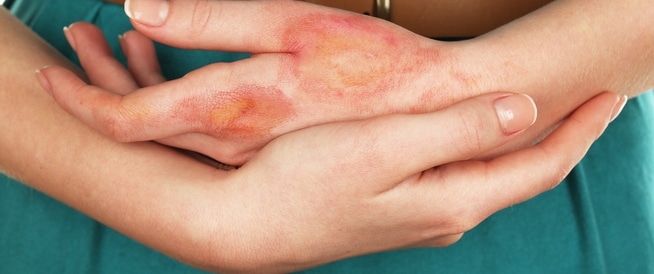
Burns, sponsored by burns, is a widespread infection, which occurs daily as talking about minor injuries. Burns Classification The burns are classified based on the degrees of their risk, as each of these grades has its own external benefits and their distinctive complications as it may require different treatment methods, which are as follows: First grade Burns: The injury is in this case only in the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). Second degree burns: are two outer layers of the skin. Third degree Burn: Damage to the layers of the skin, so it affects the tissues under the skin. Fourth degree burns: The damage is very deep layers that reach muscle, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, nerves and bones. How to calculate the affected area, the size of the affected areas is evaluated as in the following: the head and neck: 9 %. Stomach and breast: 18%. Back: 18 % every arm: 9 %. Bone: 18 %. The pubic area: 1%. Symptoms of combustion The symptoms and the incidence of the fire department differ according to its degree: The symptoms of the first grade burn are usually red or swollen skin, but permanent damage is not expected to be expected as a result of combustion like this. Symptoms of the second degree burned when exposed to the burning of this type, the skin is predominantly moist, and pimples can appear on it, and the combustion is likely to leave a chronic scar on the spot. Symptoms of the third grade burned when exposed to burning this type, the skin is usually sticky and long, and sometimes it is rough. It is possible to cause infection with the limbs of the nerves, causing tingling and numbness in the area of the injury. Symptoms of the fourth degree burned when burned from this kind are black or charred skin, and nervous injuries can be so bad and very severe to the extent of lack of pain. The causes and factors of the risk of burns. There are a large number of burns, but the most common of these types are those that result from exposure to heat directly, and one of the most important causes and the risk of combustion is burned: exposure to fire. Burning water vapor. Use hot tools. Sunlight. Electricity burned. Burning is due to chemicals, especially acidic. The complications of burns can cause other burns other than those affecting the fire area, including: The bacterial infection The skin works as a protective shield to enter harmful substances to the body, and the combustion state is harmful to this protective shield, to infiltrate pollution in the body so that it can cause local pollution in place of combustion, or that the person’s more dangerous. HypoSemia can lose due to exposure to the condition of burning a large amount of blood fluid, due to the damage of the blood vessels, and the damage of the skin we protect against fluid leakage outside. This condition can cause a decrease in the amount of blood, resulting in a low amount of blood pumping the heart to the rest of the body and causing serious damage. Reduced body temperature can lead to a large part of the skin, and if the body cannot provide the necessary heat to compensate the lost heat after this injury, the body temperature will fall in a way that threatens the life of the person with a real danger. Respiratory imbalance can inhale hot air and smoke to harm the respiratory system, which can do a lot of damage and cause a lot of breathing problems. The occurrence of scars during the natural healing process of burns can sometimes occur scars, especially if the affected tissue is external. These scars can be aesthetic, and it can also limit the ability to move when it comes over one of the body’s joints. The formation of the scars can also occur in the inner tissues, as the muscle and string tissue can pass a state of scars leading to shrinkage and the ability to move, and reduce a defect in the joint itself. Diagnosis of burns, the doctor determines the intensity of the burning based on the area it covers, after which the following tests may be needed: a blood test. X -ray. Fire treatment is related to the treatment of burns in depth and size, as this treatment of home treatment may vary if it burns slightly, to hospital treatment, if exposed to a very severe burning condition. 1. Home treatment for burns to prepare an appropriate treatment program should initially evaluate the extent of the injury and danger, the extent of the distribution of the fire and the size of the areas concerned. The treatment of the first and second degree of combustion when the first or second degree burns, which is not widespread over a large area of the body, can be treated at home in the following way: Avoid the cause of burns. The combustion is cooled with water at room temperature 10 – 25 degrees. Moisturizer to prevent the burning area from drying out, and it is recommended to use Aloe Vera. Covering the burning with sterile gauze, and it is also important not to push the fire area. Use pain relievers. Be refrained from vomiting pimples as this process increases the risk of pollution. Clean the place well with soap and water as the pimples explode, then apply an antibiotic ointment and put on the burn. In most cases, the patient does not need to see a doctor. If you are treated the third and fourth degrees of burns that burn more dangerous degrees, or in large -scale areas with a diameter of more than 7.5 inches, or burn in the palms and legs, or if you have problems after inhaling smoking, you must receive medical treatment immediately and urgently. Until the appropriate treatment is received, make sure: remove the cause of the fire from the affected area, such as: to put out burning clothes, remove the acids that led to fire and others. Make sure the injured breathes, and start the recovery process (CPR) if necessary. Cover the fire with a sterile bandage, or a clean cloth. Do not use fiber fabrics, such as: mats or towel, because these fibers can get stuck at the burning area. In these cases, a visit to the doctor should not be neglected. 2.. Medical treatment for burns. Medical treatment includes the following: Give the patient intravenously veil if the patient loses a large amount of fluid. Burning cleaning. Antibiotic therapy to prevent the spread of infection. Use pain relievers. Burning bandage. Surgery is performed during which the affected layer is removed and leather tissue is implanted in some of the cases that are very affected. Burning prevention is a common phenomenon that often occurs at home, so we must follow the following advice: to ensure that the environment around us is safe. Remove the cigarette residue and electrical plug from the reach of young children. Prevention of sun damage.
Burns: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment