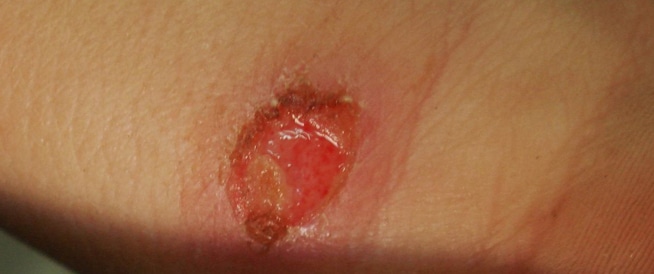
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis with sponsorship of Leishmaniac disease is a very common disease in the world of all kinds of internal and learning, as the most common species is Leishmaniac disease, as Leishmaniac disease affects the skin and leads to the appearance of ulcers, one of which reaches a few inches and recent months. Different. Lystmanias is caused by the penetration of mono -cell parasites of the type of Leishmaniac to the skin after the injured is exposed to the bite or a female sand of the Al -Fawakh family; Therefore, areas that are exposed to infection are the areas of the body that are usually not covered, such as: the surface of the face and the limbs. The parasite that causes Leishmaniac disease is a mono -cell parasite of the type of fish manica that can live and multiply in the cells of the host of the host of the host mammal, and it can also live and multiplied in the intestines of the sand fly. How does the infection occur? The parasite is transmitted to humans when exposed to the bite of the sand fly infected when stretched to an infected breast, which means that there is a triangle that is a warehouse of these parasites in nature. The fly that stitches by stitching the parasite to a person who stitches and suffers from infection, but the infection is not transferred from one person to another. The sand fly is found in most areas, where this fly is similar to a small mosquito that is no more than 1 – 3 millimeters and causes a reaction to the capacity of mosquitoes. Most sandy flies do not carry the parasite and therefore cannot transmit the infection as only in the areas concerned, that is, in which sand mice live. The flies of sand with infection can be found that can transmit the parasite by crossing, the boundaries of the affected areas can change slightly according to the changes that can occur on groups of sand mouse, but infection usually occurs when a person moves in these areas. Symptoms of Leishmaniac disease in the following clarity of the most prominent symptoms: 1. Symptoms of Leishmaniac disease depend on the symptoms of Leishmaniac disease at the place of the occurrence of pests, and this may include: Problems with breathing. Skin dozen that can become skining serve heal very slowly. Nose’s obstruction, runny nose and bleeding in the nose. Struggling to swallow. Slot and erosion in the mouth, tongue, gums, lips and inside nose. 2. Symptoms of non -local infection with children include the following: Cough. Diarrhea. fever. Vomiting. 3. The non -located symptoms in adults may include symptoms as follows: abdomen discomfort. Fever still takes months and goes and goes. Night sweat. Gray and scaly skin. Linger hair. Weight loss. Fatigue and weakness. Loss of appetite. Causes and factors of the risk of Leishmaniac disease in the following are an explanation of the most prominent causes and factors of the risk of Leishmaniac Disease: 1. Causes of Leishmaniac disease causes of Leishmaniac disease are due to the penetration of mono -parasites of the type of Leishmaniac ghost of the sand fly; Therefore, wounds are often concentrated in open areas in the body, such as: the surface of the face and the limbs. The parasite that causes the disease is a single -cell parasite of the first type of Leishmaniac, where it can live and multiply in the cells of the immune system called phagocytes of the body of the host, and it can also live and multiply in the intestines of the sand fly. 2. The risk of factors in Leishmaniac Disease includes the most important risk factors. The following: Social and economic conditions increase the poverty of the risk of Leishmaniac disease, as poor housing and home health conditions such as a lack of waste management or open sewage can lead to an increase in the multiplication of sand flying and their reaching people where the sand fly is attracted to overcrowded housing; Because it offers a good source of blood meals. Malnutrition increases the diet that does not have protein, energy, iron, vitamin A and zinc, from the risk of infection to full maturity. Environmental changes can be influenced by the rate of infection with Leishmaniasis with changes in urbanization and human invasion of forest areas. Climate change of climate Leishmaniasis is sensitive to the climate because it affects the infection of Leishmaniac disease in different ways: changes in temperatures, precipitation and humidity can have a strong effect on the vectors of the disease by changing its spread and influencing its existence. The minor fluctuations in the temperature can have a deep influence on the developmental cycle of the Leishmaniasis in the sand fly, through which the parasite can move in areas that were not endemic to the disease. Dehydration, famine and flooding can lead to collective displacement and migration of people to the areas where the Leishmaniasis are transferred, and malnutrition can harm their immunity. The complications of Leishmaniac disease include the most important complications as follows: Bleeding. Stuffed infections due to damage to immune system. Facial distortion. The diagnosis of Leishmaniac disease The diagnosis of Leishmaniac disease usually depends on the date and the clinical incidence of the pest, as the date of comprehensive journey is one of the things that help with the diagnosis of the disease, where the diagnosis can be confirmed by identifying the parasite in: biopsy or crushed skin. Take a sample mucus in the nose to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of Leishmaniah, which is important if the risk of infection with Leishmaniasis -Mukosa. In more than 70% of cases, a complete thick skin biopsy can detect the parasite, as pathological anatomy is also used to determine the Leishmaniasis -Mukosa and Leishmaniac disease. Full blood census and liver function tests must also be performed in Leishmaniac disease. Treatment of Leishmaniac disease When a single lesion of Leishmania has a scar, has a small effect that is not an aesthetic defect, so it is not necessary and it is possible to wait until the disease has disappeared automatically. If lesions occur in the face or multiple lesions in the ends, Leishmaniac disease can be treated with: ointment that kills the parasite or drugs by injection into the lesion, or intravenously during hospitalization. The most prominent treatments include the following: Paromomycin: An ointment containing Baromecin has been developed as the treatment is done by ointment over the injury. Sodium stibogluconate: This drug is given by injection into the intravenous, or within the muscle or injection into the same lesion. Leishmaniac disease prevention can prevent infection by avoiding sand flying; This is due to the lack of vaccines or medication to prevent infection, so travelers should spread to the areas where the lycemanias spread to reduce the risk of bite by holding the following precautions: Avoid external activities, especially than dusk and dawn when sand flies are more active. Wear long -sleeved shirts, long pants, socks and place the shirt in the pants. Put the insectric on the open skin and under the ends of the sleeves and bone, the most effective repulsive substances are those containing a double -ethnic chemical –Tolmamide (n -diethyl -meeta toluamide). Spray clothing, homes and sleep, including a bed bed with pesticides containing permethrin.
Lystmaniasis: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment